Privacy by Design Methodology allays Privacy Concerns in 5G Technology
What is 5G?
5G, short for "fifth generation," is the latest and most advanced cellular network technology. It is the successor to 4G (LTE) and offers a lot more benefits than 4G. It enables faster data speeds, lower latency, and greater capacity for connecting a vast number of devices simultaneously. 5G is designed to enhance mobile broadband services while enabling new applications and use cases. More specifically, the Internet of Things (IoT), virtual reality, augmented reality, and industrial automation. The deployment of 5G network brings numerous benefits.
Privacy Concerns in 5G:
Unfortunately, along with the benefits, it introduces new data privacy risks that organizations and individuals need to be aware of. Data privacy is typically associated with the proper handling of personal data or personally identifiable information (PII), such as names, and addresses.
5G networks enable the generation of higher volumes of data due to the extensive number of connected devices and its ability to transmit data at a faster speed. It involves collaborations among multiple parties, including telecom operators, service providers, and technology vendors. It can lead to increased sharing of user data among these entities, raising concerns about the control and consent of data sharing and the potential for data misuse.
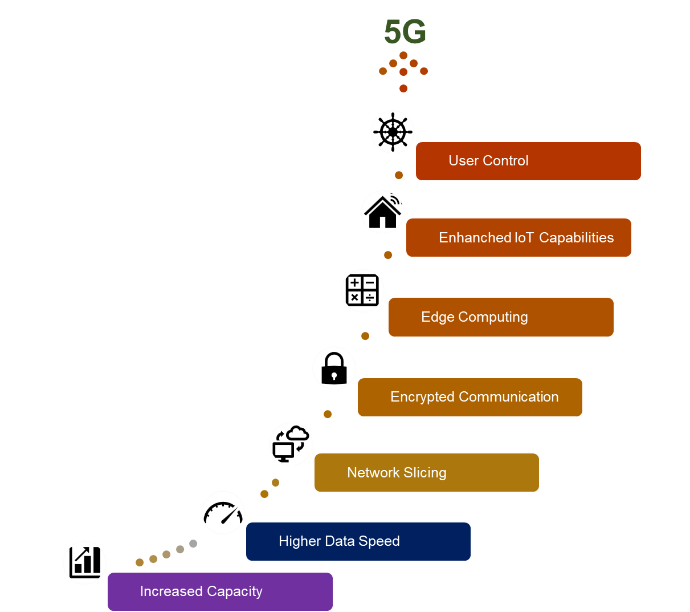
Figure: Benefits of 5G Technology
Connectivity Conundrum
The rollout of 5G technology brings new, more significant, and complex security threats because it significantly increases the attack surface by adding billions of new devices. The right to privacy may be violated because tracking is made easier with greater accuracy in 5G.
IoT will quickly proliferate due to 5G, connecting billions of devices to billions of users. The increasing number of IoT devices also portends an increase in security concerns because many IoT devices are not built with security in mind, leaving every untrusted IoT device on a company's network vulnerable to intrusions.
Privacy protection in 5G: The Way Out
Although 5G technology has the potential to create new privacy concerns, it also offers ways to deal with them. Here are a few ways that 5G can improve privacy:
- Encrypted Communication: 5G networks provide advanced encryption capabilities, increasing the security of users' data. 5G networks can prevent unauthorized access and ensure that data is only accessible to the intended recipient by encrypting data.
- Network Slicing: 5G networks enable network slicing, or the creation of virtual networks that are isolated from one another. Distinct types of data can be transmitted over separate virtual networks, each with its own security and privacy measures, which can minimize the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive data.
- Edge Computing: Through edge computing, 5G technology enables the deployment of more computing power closer to the end user. This means that data processing can occur closer to the source, minimizing the need for data to be transmitted to central processing locations, thus increasing the security and privacy of user data.
- User Control: 5G technology gives users more control over their data. For instance, users can choose to share their location data only with specific applications or services and can revoke that access at any time.
What is Privacy by Design:
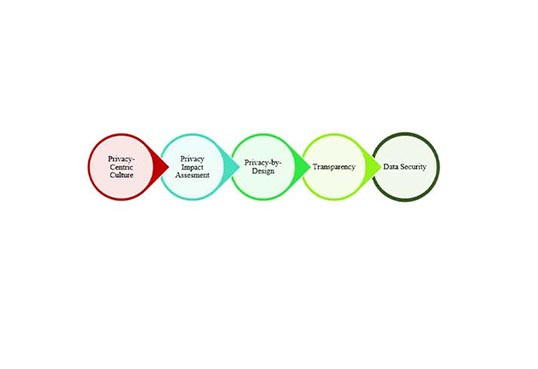
Privacy-by-Design (PbD) is a methodology that enables privacy to be ‘built in’ into the design and architecture of information systems, business processes, and networked infrastructure. PbD aims to ensure that privacy is considered before, at the start of, and throughout the development and implementation of initiatives that involve the collection and handling of personal data.
How Robi uses PbD Methodology to ensure Privacy?
Robi has incorporated the PbD methodology into the design and development of 5G networks and services. By implementing the PbD principles in 5G networks, devices, and applications, we are proactively addressing potential privacy challenges, safeguarding user data, and empowering individuals with control over their information. This builds trust in 5G and ensures that user’s privacy isn't sacrificed for technology's sake.
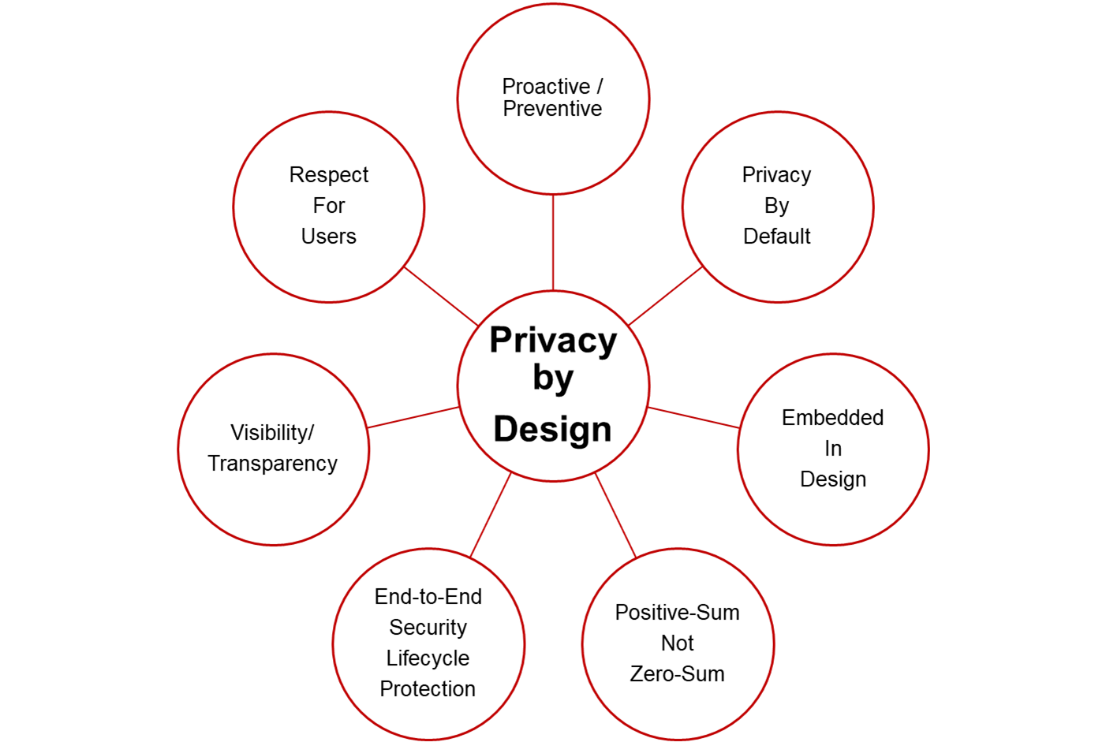
Figure: Privacy by Design Methodology
Robi’s Outlook on Privacy:
Robi ensures that everyone's privacy is respected, and that all personal data is kept secure. From gathering of requirements to designing, we follow PbD and use secure coding and testing processes in all systems to meet customers' expectations as well as regulatory requirements. We have adopted industry best practices in this connection.
Robi’s Strategy for Privacy Assurance:
Robi's strategy is always proactive rather than reactive. We foresee and prevent invasions of privacy before they occur. By ensuring that all IT systems and operational procedures implicitly safeguard personal data, we work to guarantee the highest level of privacy. PbD has been incorporated into our business procedures and IT system architecture. As a result, privacy becomes a fundamental part of the primary features offered. We aim to find solutions where everyone benefits, instead of making choices that harm one party.
Closing remarks:
As 5G networks continue to evolve, we must be vigilant about the privacy risks that arise with the increased connectivity and data processing capabilities. By incorporating PbD we expect to mitigate these risks and foster a privacy-centric approach to 5G network deployments.
Other Blogs